Cloud computing
Cloud computing is a model that provides access over a network to a collection of resources. These resources can be either physical or virtual, and they are designed to be flexible and scalable.
Users can share and manage these resources as needed. Provisioning and administration are done on-demand through self-service, making the system efficient and convenient, according to ISO.
Cloud computing explained
Cloud computing is a technology that enables you to save and retrieve data and software via the internet rather than relying on your computer’s local storage or a nearby server.
With cloud computing, you can keep various types of information—like files, pictures, videos, and documents—on remote servers and access them anytime from any internet-connected device.
What is cloud computing?
Cloud computing provides on-demand availability of various IT resources through the internet. These resources can include physical or virtual servers, storage systems, and networking solutions.
It also offers tools for application development, software platforms, and advanced AI-driven analytics. The services typically follow a pay-as-you-go model, allowing users to pay only for what they use.
Cloud computing news today
On September 24–25, 2025, the RAI in Amsterdam will be the venue for TechEx Europe. The event will bring together over 8,000 industry professionals for two full days.
The conference will feature more than 250 speakers across five parallel expos. These include the IoT Tech Expo, Cyber Security & Cloud Expo, AI & Big Data Expo, Digital Transformation Week, and the Data Centre Expo.
Cloud computing services
Cloud computing refers to using the internet to handle storage, management, and processing of data. Instead of relying on your personal computer or a local server, the tasks are carried out online. The information is kept on servers located far away.
These servers are managed by companies known as cloud providers, like Amazon, Google, and Microsoft. They offer access to their services and charge fees based on your level of usage. The more resources you use, the more you pay.
Cloud computing solutions
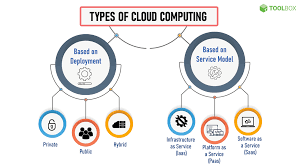
Cloud computing delivers access to digital resources such as data storage, applications, and processing power over the internet. Instead of relying on local infrastructure, users can tap into these services remotely and on demand.
This overview explains the main categories of cloud offerings: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). It also highlights the advantages they bring and how different industries apply them in practice.
Cloud computing definition
“The cloud” means servers that people connect to through the Internet, along with the software and databases that operate on them. These servers are stored inside data centers spread across the globe.
With cloud computing, individuals and businesses don’t need to handle their own physical servers. They also avoid running software directly on their personal devices.
Edge computing vs cloud computing
Cloud computing refers to a model of computing where flexible and scalable IT-based resources are provided as services through internet technologies.
Edge computing involves placing processing capabilities nearer to the source of data, typically an IoT device or sensor.
Cloud computing security
Cloud security, also known as cloud computing security, involves a wide range of strategies, tools, software, and safeguards designed to secure virtualized information, data, applications, services, and the supporting infrastructure in cloud environments.
It represents a specialized branch within computer security and network security, and is ultimately a component of the larger field of information security.
Cloud computing platform
Cloud-based solutions are created by utilizing different platforms and development frameworks. These tools make it easier to design, build, and deploy applications efficiently.
A wide range of services are offered, from raw infrastructure resources to flexible applications. They can also be tailored to meet specific business or functional needs.