Cloud computing
The origins of cloud computing date back to the 1960s, when the idea of time-sharing first emerged. During this period, remote job entry (RJE) became a popular method for accessing computing resources.
At that time, the “data center” approach was widely used, where users would submit their tasks to operators who ran them on mainframe computers. This model allowed multiple users to share computing power efficiently.
Cloud computing explained
Cloud computing relies on remote servers connected through the Internet to store, manage, and process information. These networked servers handle data without requiring local infrastructure.
Users can access cloud resources whenever they need, adjusting their usage up or down without purchasing physical hardware. Cloud services provide benefits like cost efficiency, scalability, dependability, and easy access. They help reduce capital expenses and enhance overall operational efficiency.
What is cloud computing?
The “cloud” isn’t something that floats in the sky. It actually means using remote servers—big, powerful computers stored in large data centers—through the internet.
Cloud computing lets you access these servers easily. It gives you more flexibility and the ability to scale up or down compared to having all your computers and servers on-site.
Cloud computing news today
TechEx Europe offers insights from across the sector, including businesses, regulators, and tech innovators, helping infrastructure providers understand their role within this evolving environment.
With dedicated tracks on security, digital transformation, and AI, the event allows data centre and cloud leaders to learn firsthand about the changing priorities of their customers.
Cloud computing services
These are often referred to as the cloud computing stack because each layer is built upon the one below it. Understanding what each layer does and how it differs makes achieving your objectives much simpler.
These layers can also be seen as a layered architecture, where higher-level services can be constructed using services from the layers beneath. For example, SaaS applications can rely on the underlying infrastructure to function.
Cloud computing solutions
To truly take advantage of cloud technologies, you first need to understand what “the cloud” means. Essentially, it involves using internet-based servers to handle data and applications.
These servers let people and organizations store, access, and manage information from multiple devices. This works no matter where you are physically located.
Cloud computing definition
The cloud allows people to use the same files and apps from nearly any device. This works because the computing and storage happen on servers in a data center, rather than on the device itself.
For example, if someone gets a new phone after their old one breaks, they can log into Instagram and see their account just as it was. All their photos, videos, and message history remain available.
Edge computing vs cloud computing
Cloud computing enables businesses to launch applications rapidly while requiring minimal upfront investment.
Edge can speed up understanding for applications involving sophisticated AI models that need minimal delay, such as self-driving cars and augmented reality experiences.
Cloud computing security
Cloud computing and storage allow users to save and manage their data on servers maintained by external providers. This means organizations do not need to rely solely on their own local infrastructure.
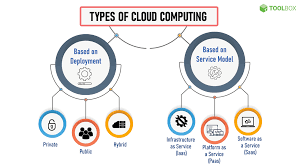
Businesses can utilize the cloud through various service models, including SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS. Additionally, they can choose different deployment options such as private, public, hybrid, or community clouds depending on their needs.
Cloud computing platform
Cloud platforms operate by providing on-demand access to computing resources. Companies lease services like servers, databases, storage, networking, analytics, software, and artificial intelligence tools.
This model removes the need for businesses to build and maintain their own data centers or hardware infrastructure. Instead, they are charged only for the resources they actually consume.