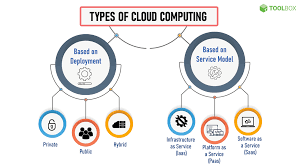
Cloud computing
One of the primary difficulties in cloud computing, compared to traditional on-site systems, is ensuring the security and privacy of data. Users rely on third-party providers to store their sensitive information, which may not always have sufficient safeguards to prevent unauthorized access, breaches, or data leaks.
Cloud computing explained
With cloud computing, there’s no need to allocate more resources than necessary in advance to manage future peak workloads. You can simply set up the resources you actually require. These resources can be adjusted up or down to quickly increase or decrease capacity. This allows your infrastructure to match your business needs as they change.
What is cloud computing?
Cloud computing allows you to shift some or all of the costs and effort involved in buying, setting up, and maintaining mainframe computers and other local infrastructure. You pay only for the cloud services and computing resources you actually use.
Cloud computing news today
You can include cloud storage plans in that category as well. Companies like Apple, Google, and Microsoft provide only a small amount of free cloud space. If you want the ease of having your photos, videos, and other files securely backed up and available on all your devices, you’ll likely need to subscribe to a paid plan.
Cloud computing services
Most SaaS applications can be used directly through a web browser without requiring downloads or installations. This saves time on setup and configuration while also minimizing potential problems during software deployment. Application data can be reached from any location.
Cloud computing solution
Cloud solutions function by utilizing a collective pool of computing resources that are flexibly assigned to users whenever required. These resources may consist of processing capacity, storage, databases, networking, and different types of software tools. Users are able to reach cloud services either through web browsers or by using application programming interfaces (APIs). This makes them easily accessible across multiple devices and from different locations.
Cloud computing definition
The foundation of cloud computing is built on back-end platforms that utilize multiple servers for processing and storing data. These servers handle application logic, ensuring efficient management of tasks and operations. Storage systems provide reliable data handling, while the combination of these back-end platforms delivers the necessary processing power and capacity to manage and store information in the cloud.
Edge computing vs cloud computing
Backing up data, recovering from disasters, and maintaining business operations become simpler and more cost-effective since information can be replicated across several redundant locations within the cloud provider’s infrastructure. When information is handled at the point of collection, edge computing enables businesses to retain all confidential data and processing within their local network and corporate firewall.
Cloud computing security
When a company chooses to store information or run applications on a public cloud, it gives up the option of physically accessing the servers that hold its data. This creates a situation where critical or sensitive information could become vulnerable. Insider threats pose a significant concern in this context. In fact, the Cloud Security Alliance identified insider attacks in its 2010 report as one of the seven most serious risks in cloud computing.
Cloud computing platform
Today, most businesses rely on a mix of cloud providers, on-premises infrastructure, and various applications within their cloud ecosystem. Handling all of these resources can quickly become complex and prone to mistakes. To bring order to this complexity, many companies adopt a cloud management platform (CMP) as part of their broader cloud orchestration approach. The ultimate objective is to create a simplified process that ensures better visibility and control.